Since the discovery of the element titanium in 1790, mankind has carried out a hundred years of painstaking exploration in order to obtain its extraordinary performance. 1910, mankind produced the metal titanium for the first time, but the application of titanium alloys was a long and arduous road, and it was not until 40 years later, in 1951, that industrial production was finally realized.
Titanium alloys are characterized by high specific strength, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance and fatigue resistance. Titanium alloys of the same size are only 60% of the weight of steel, but they are stronger than alloy steel. Because of its good characteristics, titanium alloy has been more and more widely used in the fields of aviation, aerospace, power generation equipment, nuclear energy, ships, chemical industry and medical equipment.
Titanium alloys are difficult to machine for a number of reasons
The four characteristics of titanium alloy, such as low thermal conductivity, severe work hardening, high affinity with the tool, and small plastic deformation, are the essential reasons why titanium alloy is difficult to machine. Its cut index is only 20% of that of free-cutting steel.
Low thermal conductivity
Titanium alloy thermal conductivity is only about 16% of 45 # steel, processing heat can not be conducted out in a timely manner, resulting in cutting edge local high temperature (processing tip temperature is more than 1 times that of 45 # steel), easy to trigger tool diffusion wear.
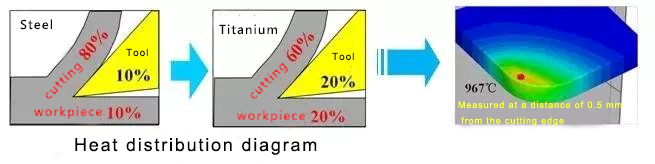
Severe work-hardening
Titanium alloy machining hardening phenomenon is obvious, the surface hardening layer compared to stainless steel is more serious, will cause some difficulties to the subsequent processing, for example, tool boundary damage increases.

High affinity to the tool
Severe bonding with titanium-containing carbide.
About 1/2 of the modulus of elasticity of 45 steel, so the elastic recovery, friction is serious. At the same time, the workpiece is also easy to clamping deformation.
Processing tips for titanium alloys
Based on the understanding of the machining mechanism of titanium alloys, together with the past experience, the main technological know-how of machining titanium alloys is as follows:
(1) The use of positive angle geometry of the insert to reduce the cutting force, cutting heat and deformation of the workpiece.
(2) maintain a constant feed to avoid hardening of the workpiece, in the cutting process, the tool should always be in the feed state, when milling, the radial cutting depth ae should be 30% of the radius
(3)The use of high-pressure, high-flow cutting fluid to ensure the thermal stability of the machining process, to prevent the workpiece surface denaturation and tool damage due to high temperature.
(4) Keep the blade edge sharp, blunt tools are the cause of heat buildup and wear, which can easily lead to tool failure.
(5) Machining of titanium alloys in the softest state possible, as the material becomes more difficult to machine after hardening, and heat treatment increases the strength of the material and increases the wear of the insert.
(6) Use a large tip radius or chamfer to cut into, as much as possible into the cutting edge of the knife. This can reduce the cutting force and heat at each point, to prevent localized breakage. In the milling of titanium alloy, the cutting speed of each cutting parameter has the greatest impact on tool life, radial draft (milling depth) followed.
Solving titanium machining problems, starting with blades
The insert groove wear that occurs when machining titanium alloys is localized wear at the back and front in the direction of the depth of cut, which is often caused by the hardened layer left by the previous machining. Tool and workpiece materials in the processing temperature of more than 800 ℃ chemical reaction and diffusion, is also one of the reasons for the formation of groove wear. Because in the machining process, the titanium molecules of the workpiece in front of the blade accumulation, in the high pressure and high temperature “welded” to the cutting edge, the formation of chip tumors. When the chipoma is stripped from the cutting edge, the carbide coating of the insert is taken away, so titanium machining requires special insert materials and geometries.
Tool construction suitable for titanium machining
The focus of titanium machining is heat, and large quantities of high-pressure cutting fluid need to be sprayed onto the cutting edge in a timely and accurate manner in order to remove the heat quickly. There are unique structures of milling cutters on the market that are specifically designed for titanium machining.
Starting with specific machining methods
Turning
Titanium alloy products turning, easy to obtain a good surface roughness, work hardening is not serious, but the cutting temperature is high, fast tool wear. For these characteristics, mainly in the tool, cutting parameters to take the following measures.
Tool material: YG6, YG8, YG10HT according to the existing conditions of the factory.
Tool geometry: suitable front and rear tool angles, tip rounding.
Lower cutting speed, moderate feed, deeper depth of cut, adequate cooling, turning cylindrical tool tip can not be higher than the center of the workpiece, otherwise it is easy to tie the knife, precision turning and turning thin-walled parts, the main tool deflection angle should be large, generally 75 ~ 90 degrees.
Milling
Titanium alloy products milling is more difficult than turning, because milling is intermittent cutting, and chips are easy to bond with the cutting edge, when the sticky chips of the cutter teeth cut into the workpiece again, the sticky chips are touched off and take away a small piece of tooling material, the formation of chipping, which greatly reduces the durability of the tool.
Milling method: generally adopt the smooth milling.
Tool Material:HSSPM/Carbide.
General alloy steel processing are not used along the milling, due to the machine tool screw, nut clearance, along the milling, the milling cutter on the workpiece, in the direction of the feed direction of the force and the same direction of the feed, easy to make the workpiece table to produce clearance fluctuations, resulting in a knife. For smooth milling, the teeth start cutting into the hard skin and lead to tool breakage. But because of the reverse milling chip is from thin to thick, in the initial cut into the tool is easy to dry friction with the workpiece, aggravated by the tool of sticky chips and chipping. In order to make titanium alloy milling smoothly, should also pay attention to relative to the general standard milling cutter, the front angle should be reduced, the rear angle should be increased. Milling speed should be low, as far as possible, the use of pointed milling cutter, avoid the use of spade tooth milling cutter.
Tapping
Titanium alloy products tapping, because the chip is small, easy to bond with the cutting edge and the workpiece, resulting in processing surface roughness value is large, torque is large. Improper selection of taps and improper operation during tapping will easily cause hardening, low processing efficiency and taps breakage.
Need to prioritize the use of a skipped thread tap in place, the number of teeth should be less than the standard tap, generally 2 ~ 3 teeth. Cutting cone angle should be large, taper part of the general 3 ~ 4 buckle thread length. In order to facilitate chip removal, but also in the cutting cone part of the negative angle of grinding. Try to use a short tap to increase the rigidity of the tap. The inverted taper part of the tap should be appropriately larger than the standard, in order to reduce the friction between the tap and the workpiece.
Reaming
Titanium alloy reaming tool wear is not serious, the use of carbide and high-speed steel reamer can be. The use of carbide reamer, to take a similar drilling process system rigidity, to prevent the reamer chipping. Titanium alloy reaming when the main problem is reamed hole finish is not good, must use oil stone repair narrow reamer edge band width, so as to avoid the edge band and the hole wall bonding, but to ensure sufficient strength, general edge width of 0.1 ~ 0.15mm is good.
Cutting edge and calibration part of the transfer should be a smooth arc, wear and tear should be timely grinding, and require the same size of the arc of the teeth; if necessary, increase the calibration part of the inverted cone.
Drilling
Titanium alloy drilling is more difficult, often in the process of burning and broken drill phenomenon. This is mainly due to poor drill sharpening, chip removal is not timely, poor cooling and process system rigidity and other reasons. Therefore, in the titanium alloy drilling process must pay attention to reasonable drill sharpening, large top angle, reduce the outer edge of the front angle, increase the outer edge of the back angle, chamfering cone added to the standard drill 2 ~ 3 times. Return the cutter diligently and remove the chips in time, pay attention to the shape and color of the chips. If the chips appear feathery or the color changes during the drilling process, it indicates that the drill bit has been blunt and should be sharpened in time.
Drill mold should be fixed on the table, the drill mold guide surface should be close to the surface of the processing, try to use a short drill. There is also a noteworthy problem is that when taking the manual feed, the drill bit should not advance or retreat in the hole, otherwise the drill edge friction processing surface, resulting in processing hardening, so that the drill dull.
Grinding
A common problem in grinding titanium alloy parts is the clogging of the grinding wheel and surface burns caused by sticky chips. The reason for this is that the poor thermal conductivity of titanium alloys generates high temperatures in the grinding zone, which leads to bonding, diffusion and strong chemical reactions between titanium alloys and abrasives. Sticky chips and wheel clogging lead to a significant reduction in the grinding ratio, the result of diffusion and chemical reaction, so that the surface of the workpiece to be ground burns, resulting in reduced fatigue strength of the parts, which is more pronounced in the grinding of titanium alloy castings.
The measures taken to address this problem are.
Choose the appropriate grinding wheel material: green silicon carbide TL. slightly lower wheel hardness: ZR1.
Cutting of titanium alloy materials, must be controlled from the tool material, cutting fluid, machining process parameters, in order to improve the comprehensive efficiency of titanium alloy materials processing.





